- Oct 9, 1999
- 5,331
- 4,016
- 136
With the release of Alder Lake less than a week away and the "Lakes" thread having turned into a nightmare to navigate I thought it might be a good time to start a discussion thread solely for Alder Lake.
It sounds like that Vegas Pro and Render+ are using dynamic cpu priority, next time see if priority changes when it goes to the background.Thread Director and Windows 11 observations with my new rig.
Last night I'm editing some video with Vegas Pro and then rendering using Render+, which is the "Happy Otter" add on for Vegas. It basically allows high quality x264/265 rendering. I notice that when Vegas is "on top" all 20 logical processors are at it but when I move to another apps the Gracemont cores take over. The thing Ian was concerned about.
I think I actually like this behavior. I was watching the UFC fight night on ESPN+ on the computer and also doing some Photoshop work so I had all of the P's at my disposal for Photoshop. The video was rendering just fine in the background and I didn't need it done immediately. Plus it can always be set to batch render.
If I was to fine tune this behavior I would have 4 P's "stay with me" on my current app while the rest stay with background processes.
But this is going to be a subjective thing, which will vary from person-to-person so I think the Thread Director is making the right decision by keeping the P's with the user. Perhaps in the future there could be a setting in Control Panel that allows you to assign P's and E's to foreground/background applications. So if you have 8 P's and 4E's like the 12700K you could select 4 P's as foreground and the rest to background as the OS deems necessary. Or if you really needed the background apps to crank you could select 2 E's for foreground for a little web browing or something?
A long time ago, I recall reading that it mainly equalizes the priority of background services so that they have a better chance of being scheduled next to run and increasing the time that a thread can run before being thread switched away and therefore increasing throughput at the cost of responsiveness. But this was in the era of a single core systems, you probably wouldn't even notice anything when systems today have so many cores and SMT.View attachment 53862
What do you suppose would happen if you select Background Services on your system? Would that make all except one P-core tend to background stuff?
But this was in the era of a single core systems, you probably wouldn't even notice anything when systems today have so many cores and SMT.
These results are better than what I feared based on the STR initial testing, as long as the small cores are still being used we're still open for further software improvements and also complete chip utilization if some games end up scaling past 8 cores. (think turn based games where AI turn time matters). Turning off the E-cores is a simple solution for now (just like staying on Win10), but in the future I'd like to use the full potential of Intel's flagship chips.It seems for gaming only, the thing to do is turn off the e-cores:
It seems for gaming only, the thing to do is turn off the e-cores:
Sure, Intel performance boost in SMT before it was 21% at best on Skylake based CPUs, with Golden Cove that boost in performance goes up to 30%I agree that's the logical expectation. Are we seeing it in practice?
Sure, Intel performance boost in SMT before it was 21% at best on Skylake based CPUs, with Golden Cove that boost in performance goes up to 30%
I seem to remember the ~20% number for most Intel systems for years(preceding alder lake), and AMD was 30%. So its good that the new Intel's as 30% also.Pretty sure it was "up to" 30% on older Intel CPU like 8700K as well.
SMT gains are an indirect measurement of how much of the CPU is sitting idle. It is great to be able to recover that performance for applications that can benefit. But it is also a measure of how overengineered the chips are and not all applications benefit from it. In an ideal world, both Intel and AMD would both be simply 30% faster and not need SMT to recover that lost performance.I seem to remember the ~20% number for most Intel systems for years(preceding alder lake), and AMD was 30%. So its good that the new Intel's as 30% also.
I seem to remember the ~20% number for most Intel systems for years(preceding alder lake), and AMD was 30%. So its good that the new Intel's as 30% also.

 www.aeco.space
www.aeco.space
the HT provides 29% more performance compared to no HT
 www.techspot.com
www.techspot.com
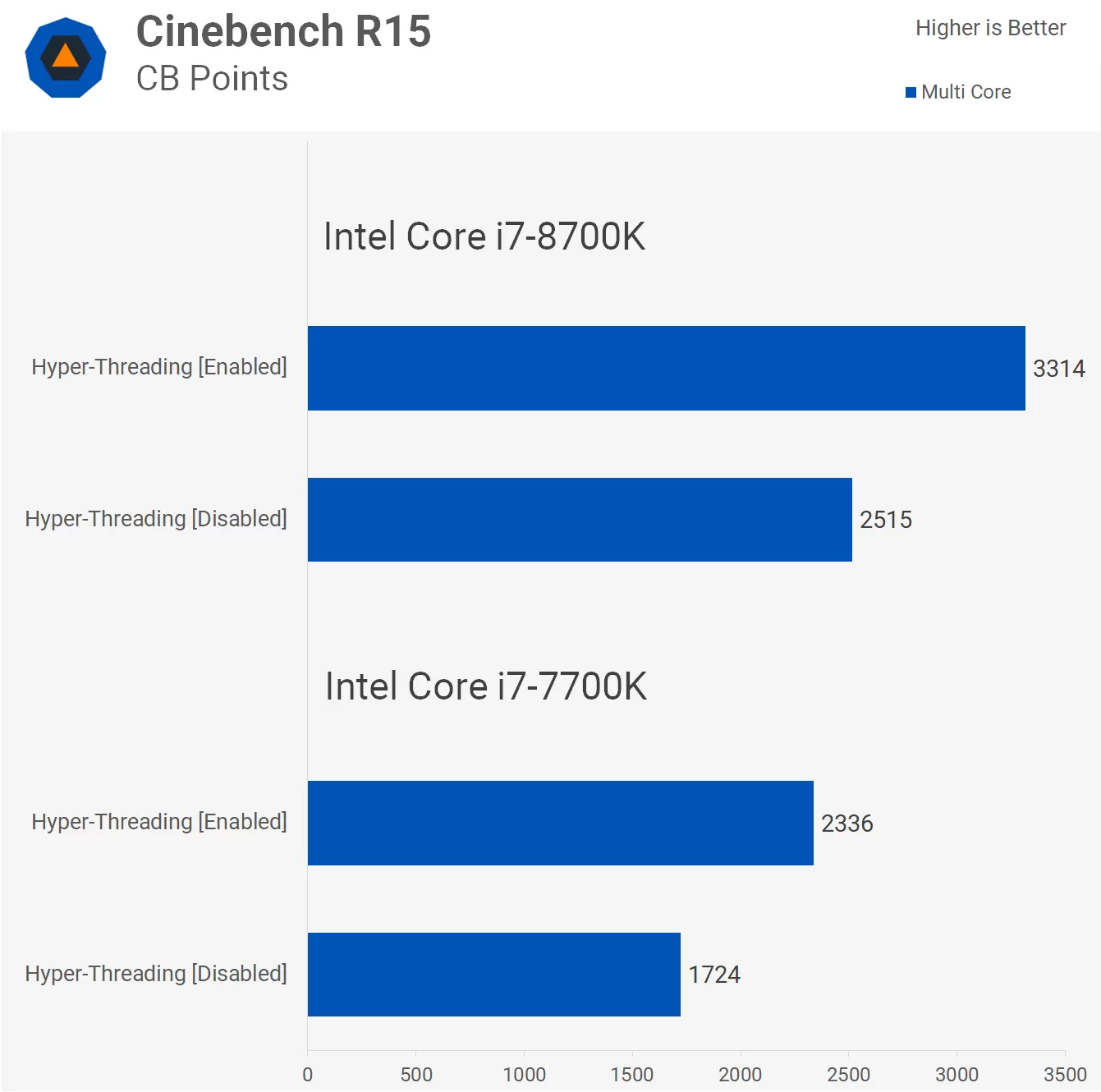
One thing to note is that benchmark is about the ideal situation to show off SMT. It will be near the top end of gains. A lot of other software show much more moderate gains. Some rare software has performance losses with SMT.Here's a HT/No HT test on the 8700K:
One thing to note is that benchmark is about the ideal situation to show off SMT. It will be near the top end of gains. A lot of other software show much more moderate gains. Some rare software has performance losses with SMT.
It's not a secret that AMD SMT from OG Zen has been extracting more performance from it's wide cores if compared to Intel Skylake based CPUs, this has changed since their new Sony Cove/Cypress Cove wider cores, they are about even now about 30%
To be honest, I was speculating on the Sunny Cove/Cypress Cove part as they are a new uArch as opposed to an evolution of the Skylake uArchSunny Cove gains weren't as good as AMD's. The consensus is that AMD got greater gains and only with Golden Cove Intel changed that.
Can you Elaborate on this Fascinating Subject? As far as I am aware way back on the old Pentium 4 days, Intel spent 5% die area for a maxium 20% performance uplift, but I am not sure if this has been remain the same all the way to Alder lake.I suspect Intel wanted to prioritize for single thread performance by going for a more unified approach(So resources will be split into two with HT) while AMD went for a distributed approach because that'll result in better SMT gains. The "unified vs distributed" design philosophy between the Core team and AMD's team is pervasive. AMD went for a more distributed scheduler design and Intel a unified Int/FP scheduler for example.

No it's not, just as you yourself mentioned "SMT gains are an indirect measurement of how much of the CPU is sitting idle. " software that uses the least amount of CPU resources would be the most ideal situation, things like games or general windows usage where threads are just made to do what they need instead of software that does all the compute it can get it's hands on.One thing to note is that benchmark is about the ideal situation to show off SMT. It will be near the top end of gains. A lot of other software show much more moderate gains. Some rare software has performance losses with SMT.
Has AMD disclose how much of the Die Size they are using for SMT?
Not sure about that, at least when it comes to i7-1165G7. It was 65 degrees without HT but with HT, it was hitting 95 degrees in the TPU ThrottleStop stress test.but it sure is pretty power efficient and uses next to no transistors.